China's Rare Earth Export Curbs Hamper Tesla's Optimus Robot Development
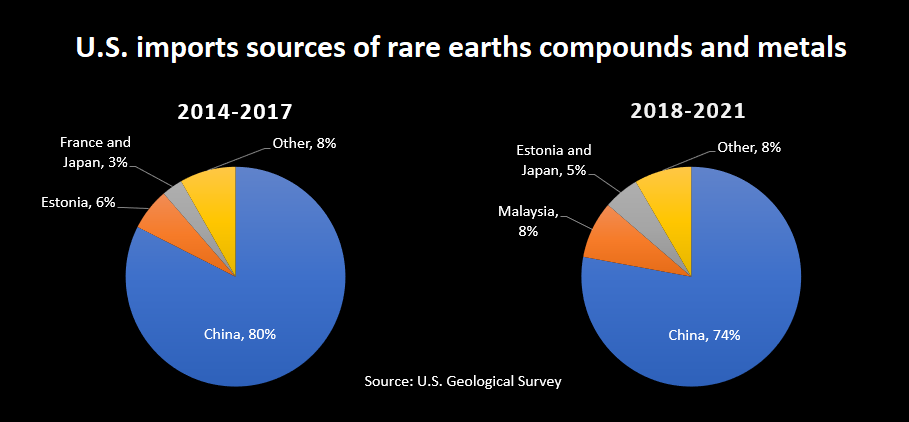
Table of Contents
China's Dominance in Rare Earth Production and its Geopolitical Implications
China's control over the rare earth market is undeniable. It holds a commanding majority of the global rare earth mining and processing capacity, a position that grants it significant leverage in international trade negotiations. This dominance translates to geopolitical risk; even subtle export restrictions can severely impact the global availability of these vital materials. The strategic importance of rare earths in various high-tech sectors, including robotics, renewable energy, and defense, is fueling growing geopolitical tensions.
- China controls over 80% of global rare earth processing capacity. This concentration gives them significant influence on pricing and supply.
- Export quotas and tariffs can be used as leverage. China has a history of using its rare earth dominance to influence international relations.
- Diversification efforts by other countries are underway but slow. Building robust alternative supply chains takes significant time and investment.
- The strategic nature of rare earths necessitates proactive geopolitical strategies. Countries are increasingly looking for ways to secure their supply chains.
The Critical Role of Rare Earths in Optimus Robot Manufacturing
The smooth operation of Tesla's Optimus robot hinges on the efficient use of rare earth elements. These materials are crucial for the high-performance motors, precision sensors, and actuators that allow the robot to move, perceive its environment, and perform complex tasks.
- Neodymium and dysprosium magnets are fundamental to Optimus's powerful motors. These magnets provide the high power-to-weight ratio necessary for efficient robot movement.
- Precise sensors rely on rare earth materials for their sensitivity and accuracy. This enables Optimus to accurately perceive and react to its surroundings.
- Actuators, which control the robot's movements, require rare earth elements for optimal performance. These components are essential for the robot's dexterity and precision.
- Disruptions in the rare earth supply chain directly impact Optimus's production costs, timelines, and overall functionality. Securing a stable supply is paramount.
Specific Rare Earths Used in Optimus and Their Sources
Optimus's functionality relies on a variety of rare earth elements, including neodymium and dysprosium in its high-torque motors, and other elements like praseodymium and terbium in various sensors and electronic components. Currently, a significant portion of these elements are sourced from China, creating a dependence that Tesla must address.
- Neodymium and dysprosium are primarily used in the permanent magnets of the robot's motors. Their strong magnetic properties are essential for generating the required torque.
- Praseodymium and terbium find applications in various sensors and control systems. These elements contribute to the robot's accuracy and responsiveness.
- The current geographical concentration of these resources in China presents a significant risk. Diversification of sourcing is critical for long-term sustainability.
Tesla's Strategies to Mitigate Rare Earth Dependence
Tesla faces a considerable challenge in securing a reliable supply of rare earth elements. To mitigate its dependence on China, the company is likely exploring several strategies.
- Supply chain diversification: Tesla may be actively seeking alternative sources of rare earths from countries like Australia, Canada, and the United States.
- Alternative materials research: Exploring alternative materials and designs that reduce or eliminate the need for rare earths in key components.
- Vertical integration: Investing in rare earth mining or processing operations to gain greater control over its supply chain.
- Recycling and resource recovery: Implementing robust recycling programs to recover and reuse rare earth elements from end-of-life products.
Conclusion
China's control over rare earth exports presents a serious challenge to Tesla's Optimus robot development and the broader field of advanced robotics. The reliance on these crucial materials underscores the vulnerability of high-tech industries to geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions. Tesla's success in overcoming this hurdle will hinge on its ability to diversify its sourcing, explore alternative materials, and potentially engage in vertical integration of its supply chain. The future of advanced robotics, exemplified by Tesla's Optimus, is inextricably linked to the global rare earth landscape. Further research and dialogue on securing reliable and ethical rare earth sourcing are crucial for the continued development and success of advanced robotics and for mitigating the risks inherent in China's rare earth export policies.

Featured Posts
-
 Open Ais Chat Gpt Under Ftc Scrutiny A Deep Dive Into The Investigation
Apr 24, 2025
Open Ais Chat Gpt Under Ftc Scrutiny A Deep Dive Into The Investigation
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Office365 Executive Inbox Hacks Net Millions Federal Investigation Reveals
Apr 24, 2025
Office365 Executive Inbox Hacks Net Millions Federal Investigation Reveals
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Eu To Discuss Phasing Out Russian Gas Via Spot Market Targeting
Apr 24, 2025
Eu To Discuss Phasing Out Russian Gas Via Spot Market Targeting
Apr 24, 2025 -
 India Saudi Arabia Partner For Two New Oil Refineries
Apr 24, 2025
India Saudi Arabia Partner For Two New Oil Refineries
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Nba All Star Weekend Green Moody And Hield Among The Participants
Apr 24, 2025
Nba All Star Weekend Green Moody And Hield Among The Participants
Apr 24, 2025
