Credit Weekly: Examining The Widening Cracks In The Private Credit Market

Table of Contents
Rising Interest Rates and Their Impact on Private Credit
The sharp increase in interest rates implemented by central banks globally has significantly impacted the private credit market. This has manifested in two primary ways: increased borrowing costs for companies and reduced investor appetite for private credit investments.
Increased Borrowing Costs
Rising interest rates directly translate into higher borrowing costs for companies reliant on private credit. This makes servicing existing debt more challenging and significantly increases the likelihood of defaults.
-
Impact on various private credit products: Direct lending, a cornerstone of the private credit market, is directly affected by higher interest rates. Borrowers face escalating interest payments, straining their cash flows. Collateralized loan obligations (CLOs), which pool various loans, also see increased default risk as underlying loan payments become more difficult to meet. Leveraged buyouts (LBOs), heavily reliant on debt financing, are particularly vulnerable, as the increased cost of debt reduces the profitability of these transactions.
-
Data and Statistics: According to [Source], the default rate for private credit loans increased by [Percentage]% in the last quarter, a stark indication of the pressure mounting on borrowers. Furthermore, [Source] shows a [Percentage]% increase in the average interest rate on new private credit loans.
Reduced Investor Appetite
Higher interest rates make alternative investment options, such as government bonds, more attractive. This shift in investor preferences leads to decreased fund flows into the private credit market.
-
Shift in Investor Sentiment: Investors are increasingly wary of the increased risk in the private credit market, particularly given the potential for defaults in a higher interest rate environment. This is reflected in the reduced demand for new private credit offerings and the decreased valuations of existing investments.
-
Decreased Fund Flows: Several private credit funds have reported decreased fundraising activity in recent months, signaling a reduced investor appetite for this asset class. This lack of fresh capital is further straining the market.
The Growing Concern of Over-Leveraging in Private Credit Deals
Another significant factor contributing to the instability in the private credit market is the increasing level of leverage in private credit deals. This, combined with inadequate due diligence, presents a substantial risk.
Increased Debt Levels
Companies are increasingly relying on debt financing, often to fund acquisitions or expansion projects. This high level of leverage makes them highly vulnerable to economic downturns and rising interest rates.
-
Statistics on Leverage Ratios: The average leverage ratio for companies accessing private credit has increased significantly in recent years, according to [Source]. This increased reliance on debt leaves companies with little financial cushion to absorb unexpected shocks.
-
Examples of Highly Leveraged Transactions: Several high-profile leveraged buyouts have been completed recently with exceptionally high debt levels, highlighting the prevalent risk-taking in the market.
-
Industry-Specific Examples: The [Industry] sector, characterized by high capital expenditure needs, has seen a particularly dramatic rise in leverage.
Inadequate Due Diligence
The underwriting process for many private credit deals has faced scrutiny, with concerns raised about inadequate due diligence. This contributes to increased risk and a higher likelihood of defaults.
-
Examples of Inadequate Due Diligence: In several instances, lenders have been criticized for insufficiently assessing the creditworthiness of borrowers or overlooking key risk factors.
-
Challenges in Assessing Borrower Risk: The lack of standardized reporting and transparency in the private credit market makes it challenging to accurately assess borrower risk. This opacity is exacerbated by the often illiquid nature of private credit assets.
-
Regulatory Oversight Gaps: The regulatory framework overseeing private credit is often less stringent compared to public markets, leading to potential gaps in oversight.
Liquidity Concerns and the Challenges of Exiting Private Credit Investments
The private credit market suffers from inherent illiquidity, which poses significant challenges, particularly during market downturns. This illiquidity, combined with the potential for contagion, further amplifies the risks.
Illiquidity of Private Credit Assets
Unlike publicly traded bonds, private credit investments are not easily sold. This lack of liquidity can make it difficult for investors to exit their positions quickly, especially during times of market stress.
-
Nature of Illiquidity: The illiquid nature stems from the bespoke nature of private credit loans, lack of established secondary markets, and information asymmetry.
-
Consequences of Illiquidity: Investors might face significant losses when forced to sell their private credit investments at distressed prices during market downturns. This can trigger a sell-off further depressing values.
-
Impact of Market Volatility: Market volatility exacerbates the illiquidity problem. During periods of uncertainty, investors become more reluctant to buy private credit assets, making it harder to sell existing investments.
Potential for Contagion
Defaults in the private credit market can trigger a domino effect, leading to widespread contagion. This interconnectedness magnifies the risk.
-
Interconnectedness of the Market: The private credit market is interconnected through various relationships between lenders, borrowers, and investors. A default by one borrower can trigger a chain reaction impacting other players.
-
Mechanisms of Contagion: The contagion can spread through various channels, such as reduced investor confidence, decreased lending activity, and cross-default provisions in loan agreements.
-
Potential Impact on the Broader Financial System: If the contagion spreads widely, it could potentially destabilize the broader financial system, posing systemic risk.
Conclusion
This Credit Weekly analysis highlights significant risks and vulnerabilities within the private credit market. Rising interest rates, over-leveraging, and liquidity concerns are creating widening cracks in this previously robust investment space, increasing private credit risk substantially. The potential for contagion further compounds these risks, underscoring the need for careful monitoring and proactive risk management.
Understanding the widening cracks in the private credit market is crucial for investors and lenders alike. Stay informed about the latest developments by subscribing to our newsletter [link to newsletter] or visiting our website [link to website] to navigate the evolving landscape of private credit risk and make informed decisions regarding private credit investing and private credit analysis. Managing private credit risk effectively is paramount in today's challenging economic environment.

Featured Posts
-
 Juliette Binoche Cannes Film Festival Jury President 2025
Apr 27, 2025
Juliette Binoche Cannes Film Festival Jury President 2025
Apr 27, 2025 -
 The Night Robert Pattinson Couldnt Sleep After Watching A Horror Film
Apr 27, 2025
The Night Robert Pattinson Couldnt Sleep After Watching A Horror Film
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ecb Task Force Aims To Simplify Complex Banking Rules
Apr 27, 2025
Ecb Task Force Aims To Simplify Complex Banking Rules
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Nosferatu The Vampyre A Now Toronto Detour
Apr 27, 2025
Nosferatu The Vampyre A Now Toronto Detour
Apr 27, 2025 -
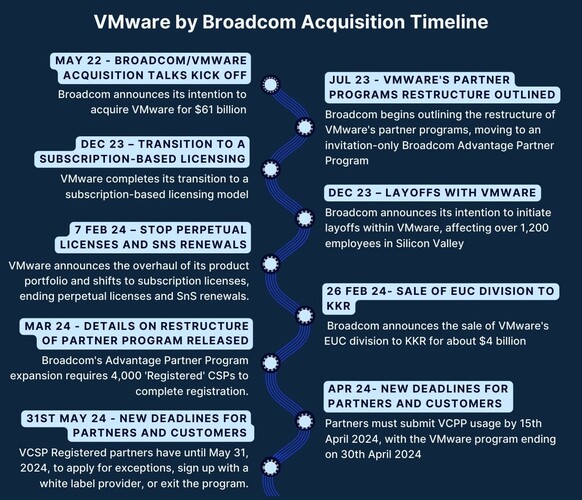 Extreme Price Increase Projected For V Mware Following Broadcom Acquisition
Apr 27, 2025
Extreme Price Increase Projected For V Mware Following Broadcom Acquisition
Apr 27, 2025
