Ohio Train Derailment: Persistent Toxic Chemical Contamination In Buildings
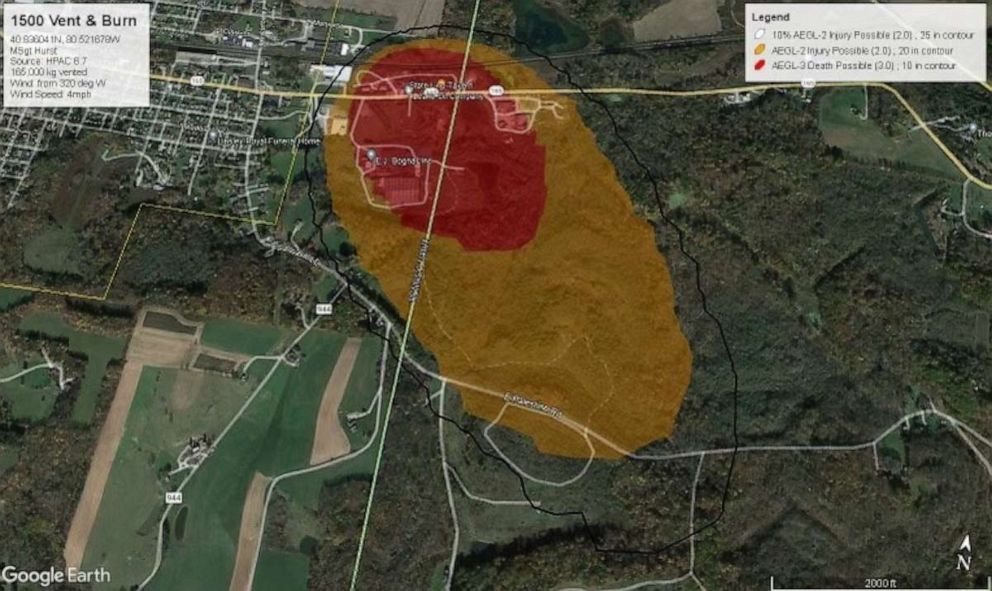
Table of Contents
Types of Persistent Contamination
The derailment released a cocktail of toxic chemicals, with vinyl chloride being the most prominent and concerning due to its volatile and persistent nature.
Vinyl Chloride Residues
Vinyl chloride, a known carcinogen, readily permeates porous materials. Its persistence in various building materials presents a long-term health hazard.
- Affected Building Materials: Vinyl chloride can penetrate drywall, insulation, carpets, fabrics, and even HVAC systems, making complete remediation extremely challenging. It can also settle into cracks and crevices, making it difficult to detect and remove.
- Long-Term Health Effects: Prolonged exposure to vinyl chloride, even at low levels, is linked to an increased risk of liver cancer, brain tumors, and other serious health issues. The long latency period between exposure and the onset of symptoms further complicates diagnosis and treatment.
- Detection and Remediation Challenges: The insidious nature of vinyl chloride contamination makes detection and remediation difficult. Specialized equipment and experienced professionals are required to accurately assess the extent of contamination and implement effective cleanup strategies. Simple surface cleaning is often insufficient.
Other Hazardous Chemicals
Beyond vinyl chloride, the derailment released other hazardous substances with varying degrees of persistence.
- Other Significant Chemicals: Butyl acrylate, ethylhexyl acrylate, and ethylene glycol monobutyl ether are examples of other chemicals released, each presenting unique risks and persistence characteristics within building materials. These chemicals can also interact with each other, creating even more complex and unpredictable contamination patterns.
- Effects on Building Materials: These chemicals can interact differently with various building materials, leading to unpredictable levels of contamination. Some may bind to surfaces more readily than others, increasing the difficulty of removing them completely.
- Health Risks of Long-Term Exposure: The long-term health consequences associated with exposure to these chemicals, individually and in combination, are still being researched, highlighting the urgent need for ongoing monitoring and investigation. Many of these chemicals are known irritants or have links to long-term health problems.
Secondary Contamination
The initial release of chemicals isn't the only source of contamination. Secondary contamination pathways further complicate the issue.
- Mechanisms of Secondary Contamination: Runoff from contaminated areas can spread chemicals into soil and water sources, which can then migrate into buildings. Air currents can also carry airborne contaminants, depositing them on surfaces within structures. The movement of contaminated debris during cleanup efforts can also inadvertently spread the contamination.
- Examples of Secondary Contamination Pathways: Contaminated rainwater flowing into basements, contaminated dust settling on surfaces, and the transfer of contaminants through contaminated clothing or equipment are all examples of secondary contamination pathways.
- Potential Spread to Unaffected Areas: Secondary contamination can significantly expand the affected area, requiring a broader and more comprehensive remediation strategy. This highlights the importance of effective containment measures during the initial response and subsequent cleanup efforts.
Impact on Building Inhabitants and the Environment
The persistent toxic chemical contamination has far-reaching consequences for the health of residents, the environment, and the local economy.
Health Concerns
Prolonged exposure to low levels of toxic chemicals released in the derailment poses significant health risks.
- Specific Health Problems: Respiratory problems, headaches, nausea, skin irritation, and other symptoms have been reported by residents in the affected area. Long-term health effects, including various cancers and neurological disorders, remain a concern.
- Long-Term Health Consequences: The long-term health impact of chronic, low-level exposure to these chemicals is still largely unknown and requires extensive long-term monitoring. This necessitates comprehensive health surveillance programs for affected residents.
- Importance of Monitoring Health Conditions: Regular health screenings and comprehensive medical records are crucial to identify and address potential health problems resulting from this contamination. Early detection is key to effective treatment.
Environmental Impacts
The persistent contamination extends far beyond building structures, impacting the surrounding environment.
- Effects on Soil and Water Quality: Contamination of soil and water sources poses a long-term threat to the local ecosystem and human health. The chemicals can leach into groundwater and contaminate drinking water supplies.
- Impact on Local Wildlife: Exposure to toxic chemicals can harm local wildlife populations, disrupting the delicate balance of the ecosystem. This includes impacts on plant and animal life.
- Potential Long-Term Ecological Effects: The long-term ecological consequences of this contamination are difficult to predict, highlighting the importance of monitoring and restoring affected ecosystems.
Economic Impacts
The consequences of the derailment extend to the local economy.
- Decreased Property Values: The persistent threat of contamination can significantly reduce property values in the affected area, impacting homeowners and the local economy.
- Cost of Cleanup and Remediation: The extensive and complex cleanup and remediation efforts will represent a substantial financial burden for both the government and affected property owners.
- Business Disruption and Economic Losses: Businesses in the affected area may suffer losses due to disruptions, closures, and reduced consumer confidence.
Remediation and Ongoing Efforts
Addressing the persistent toxic chemical contamination requires a multi-pronged approach.
Current Remediation Strategies
Efforts are underway to remediate contaminated buildings, but challenges remain.
- Methods Used for Cleaning and Remediation: Various methods, including specialized cleaning techniques, air scrubbing, and removal of contaminated materials, are being employed. The choice of method depends on the type of material and the extent of contamination.
- Difficulties in Complete Removal: Completely removing persistent chemicals from porous materials and complex building systems is extremely challenging. Traces may remain even after extensive cleanup, posing long-term health risks.
- Limitations of Current Technology: Current technologies may not be sufficient to fully address the unique challenges posed by this type of contamination, highlighting the need for advancements in remediation strategies.
Future Research Needs
Further research is essential to address knowledge gaps.
- Specific Research Areas: Research on the long-term health effects of low-level exposure, development of more effective remediation techniques, and improving detection methods are all critically needed.
- Need for Improved Testing and Detection Methods: More sensitive and reliable methods are needed to accurately detect and quantify the presence of these chemicals in various materials and environmental samples.
- Development of More Effective Cleanup Strategies: Innovative technologies and strategies are essential to effectively remove these persistent contaminants from buildings and the environment.
Governmental Response and Accountability
Governmental action is critical for accountability and preventing future incidents.
- Governmental Actions and Policies: Stronger regulations are needed to prevent future derailments and improve response to chemical spills. This includes improving track maintenance and rail car safety standards.
- Investigations into the Cause of the Derailment: Thorough investigations are crucial to identify the root causes of the derailment and implement appropriate preventative measures.
- Measures to Prevent Future Incidents: Investing in infrastructure improvements and implementing stricter safety regulations are paramount to preventing similar catastrophic events in the future.
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment's lasting impact is clearly demonstrated by the persistent toxic chemical contamination in buildings. The long-term health and environmental risks associated with this contamination are significant and require sustained attention. The challenges of complete remediation, the need for ongoing health monitoring, and the imperative to prevent future incidents highlight the gravity of this situation. Continued research, effective remediation efforts, and a commitment to stricter safety regulations are crucial to mitigating the lingering effects of this disaster and preventing similar catastrophes. We must remain vigilant in addressing the persistent toxic chemical contamination in buildings and advocate for stronger policies to protect communities from the devastating consequences of hazardous material spills.

Featured Posts
-
 Hhs Uses Anti Vaccine Advocate To Investigate Debunked Autism Vaccine Connection
Apr 27, 2025
Hhs Uses Anti Vaccine Advocate To Investigate Debunked Autism Vaccine Connection
Apr 27, 2025 -
 The China Factor Analyzing The Struggles Of Bmw Porsche And Other Automakers
Apr 27, 2025
The China Factor Analyzing The Struggles Of Bmw Porsche And Other Automakers
Apr 27, 2025 -
 The Credit Weekly Report Signs Of Stress In The Private Credit Market Before Recent Events
Apr 27, 2025
The Credit Weekly Report Signs Of Stress In The Private Credit Market Before Recent Events
Apr 27, 2025 -
 The Zuckerberg Trump Dynamic Implications For The Tech Industry
Apr 27, 2025
The Zuckerberg Trump Dynamic Implications For The Tech Industry
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ariana Grandes Hair Transformation A Look At The Styling And Tattoo Choices
Apr 27, 2025
Ariana Grandes Hair Transformation A Look At The Styling And Tattoo Choices
Apr 27, 2025
