Will Google Be Broken Up? Examining The Antitrust Challenges

Table of Contents
The question of whether Google will be broken up is increasingly prominent in the global conversation. Concerns over Google's dominant market position and potential anti-competitive practices have fueled numerous antitrust investigations and lawsuits across the world. This article delves into the key challenges Google faces, exploring the arguments for and against its breakup and assessing the potential consequences. The implications of a potential Google breakup are far-reaching, impacting not only the tech giant itself but also the broader digital landscape and consumers worldwide.
Google's Dominance Across Multiple Markets
Google's dominance is not confined to a single market; it extends across several key sectors, raising significant antitrust concerns. This widespread influence fuels the debate surrounding a potential Google breakup.
-
Google's near-monopoly in search engine market share: Google's search engine holds an unparalleled global market share, consistently exceeding 90% in many regions. This dominance gives Google immense power over information access and online advertising. This near-monopoly position allows them to control the flow of information and manipulate search results, potentially disadvantaging competitors.
-
Android's widespread adoption and its implications for the mobile operating system market: Android, Google's mobile operating system, powers a vast majority of smartphones globally. This dominance gives Google significant control over the mobile ecosystem, influencing app development, distribution, and user experience. The sheer scale of Android's adoption raises concerns about potential anti-competitive practices within the mobile app market.
-
Google's control over a significant portion of the online advertising market and its impact on competitors: Google's advertising platforms, including AdWords and AdSense, command a substantial share of the digital advertising market. This allows Google to exert significant influence over how businesses reach consumers online, potentially squeezing out smaller competitors and hindering innovation. This market concentration raises concerns about the fairness and competitiveness of the online advertising ecosystem.
-
Google Play Store's influence on app distribution and its potential for anti-competitive practices: The Google Play Store is the primary app distribution platform for Android devices. This gatekeeping role gives Google significant power over app developers, potentially enabling anti-competitive practices such as imposing unfair fees or favoring its own apps. This control limits the choices available to consumers and can stifle innovation within the app development community.
Bullet Points:
- Google's search market share consistently exceeds 90% in many countries.
- Android holds over 70% of the global mobile operating system market.
- Google's share of the digital advertising market is estimated to be around 40%.
- Google Play Store is the dominant app store for Android, holding a near-monopoly.
Antitrust Lawsuits and Investigations
Numerous antitrust lawsuits and investigations against Google highlight concerns regarding its market dominance and potential anti-competitive behavior. These legal battles have played a significant role in shaping the debate surrounding a potential Google breakup.
-
Summary of major antitrust lawsuits filed against Google (e.g., DOJ, FTC, EU): The Department of Justice (DOJ), the Federal Trade Commission (FTC), and the European Commission have all launched significant antitrust investigations and lawsuits against Google over the years, alleging various anti-competitive practices. These lawsuits cover a wide range of Google's activities, reflecting the breadth of its market power.
-
Details of the allegations in these lawsuits, including specific anti-competitive practices: Allegations include favoring Google's own products in search results (search bias), imposing restrictions on Android device manufacturers (Android anti-trust issues), and abusing its dominance in the online advertising market.
-
Outcomes of significant legal battles and their impact on Google's operations: While some cases have resulted in significant fines, others have been dismissed or settled with stipulations that haven’t fundamentally altered Google's market position. The varying outcomes highlight the complexities of antitrust litigation and the challenges in effectively addressing the power of tech giants.
-
Discussion of ongoing investigations and their potential ramifications: Ongoing investigations continue to scrutinize Google's practices, suggesting the antitrust concerns are far from resolved. The potential outcomes of these investigations could significantly impact Google's future and potentially lead to a breakup or other structural changes.
Bullet Points:
- The EU has imposed billions of euros in fines on Google for anti-competitive practices.
- The DOJ and FTC have also launched investigations into Google’s business practices.
- Ongoing investigations could lead to further fines or structural changes.
Arguments For and Against Breaking Up Google
The debate surrounding a potential Google breakup is characterized by strong arguments on both sides. Understanding these opposing viewpoints is crucial for evaluating the potential implications of such a drastic measure.
-
Arguments in favor of a breakup: Proponents argue that breaking up Google would increase competition, foster innovation, and protect consumer welfare. A fragmented market would likely lead to more diverse offerings, lower prices, and enhanced consumer choice. Increased competition would also encourage innovation as companies strive to gain market share.
-
Arguments against a breakup: Opponents argue that a Google breakup could stifle innovation, lead to higher prices, and create logistical nightmares. They suggest that Google's scale allows for significant investments in research and development, benefiting consumers through advanced technologies and services. The complexities of dividing such a large and integrated company are also significant concerns.
-
Discussion of alternative remedies to a complete breakup, such as structural separation or behavioral remedies: Instead of a full breakup, less drastic measures, such as structural separation of certain divisions or behavioral remedies to address specific anti-competitive practices, could be considered. These approaches could potentially mitigate concerns without the disruptive effects of a complete breakup.
Bullet Points:
- Increased competition could lead to lower prices and more innovation.
- A breakup could disrupt Google's ecosystem and hinder R&D investments.
- Behavioral remedies may be a less disruptive alternative to a full breakup.
The Future of Google and the Tech Landscape
The potential breakup of Google would have far-reaching implications for the tech landscape and the broader economy. Understanding these potential consequences is crucial for informed discussion and policymaking.
-
Analysis of the potential impact of a Google breakup on the broader tech industry: A Google breakup would likely reshape the competitive dynamics within the tech industry, potentially triggering a wave of consolidation and new entrants. It would also create uncertainty and necessitate significant adjustments for businesses that rely on Google’s services.
-
Discussion of the implications for consumers, businesses, and innovation: Consumers could potentially benefit from increased choice and lower prices, but they might also face disruptions in services. Businesses might face new challenges in accessing Google's services and adapting to the altered market landscape. The impact on innovation is complex and potentially both positive and negative.
-
Exploration of potential future regulatory changes and their effect on Google and other tech giants: The ongoing debate surrounding the regulation of digital monopolies is likely to continue, shaping the regulatory environment for Google and other tech giants for years to come. Increased regulation could further limit the power of these companies, but it could also stifle innovation if not carefully designed.
Bullet Points:
- A Google breakup could create new opportunities for smaller tech companies.
- Consumers might see increased competition and potentially lower prices.
- Future regulations will likely shape the competitive landscape for years to come.
Conclusion
This article has explored the complex issue of whether Google should be broken up, examining its dominant market positions, the ongoing antitrust challenges, and the arguments for and against its disintegration. The potential consequences of such a drastic measure are significant, impacting not only Google but the broader tech landscape and consumer experience. The debate surrounding the future of Google and similar tech giants is far from over. Stay informed about the ongoing developments in the Google antitrust cases and the wider discussion on regulating digital monopolies. Understanding the complexities of the Google breakup debate is crucial for navigating the evolving digital world.

Featured Posts
-
 New Business Hot Spots Where To Invest And Grow In Country Name
Apr 22, 2025
New Business Hot Spots Where To Invest And Grow In Country Name
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Trumps Protectionist Policies Impact On Us Global Financial Dominance
Apr 22, 2025
Trumps Protectionist Policies Impact On Us Global Financial Dominance
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Is Betting On Wildfires A Sign Of The Times The Los Angeles Case
Apr 22, 2025
Is Betting On Wildfires A Sign Of The Times The Los Angeles Case
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Market Rally Defies Concerns Are Investors Too Optimistic
Apr 22, 2025
Market Rally Defies Concerns Are Investors Too Optimistic
Apr 22, 2025 -
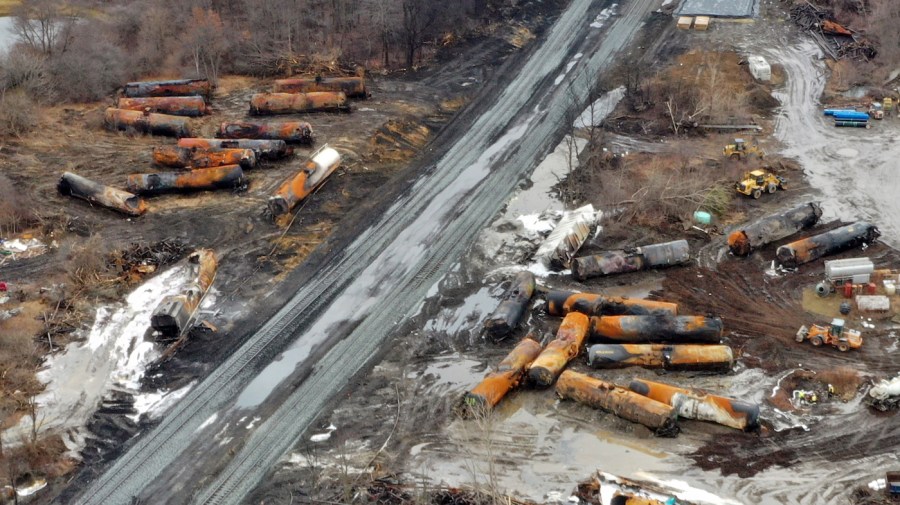 East Palestines Lingering Threat Toxic Chemicals From Train Derailment Remain In Buildings
Apr 22, 2025
East Palestines Lingering Threat Toxic Chemicals From Train Derailment Remain In Buildings
Apr 22, 2025
